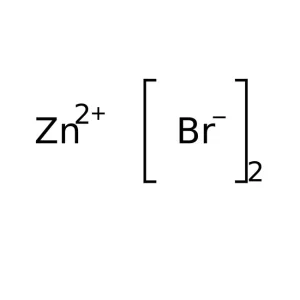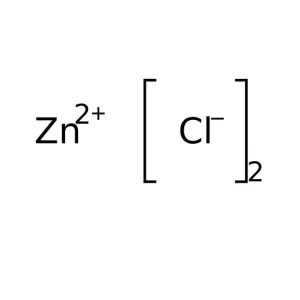Chemicals
Showing 441–460 of 466 results
-
Chemicals
Wax
Waxes are a diverse class of organic compounds that are lipophilic, malleable solids near ambient temperatures. They include higher alkanes and lipids, typically with melting points above about 40 °C (104 °F), melting to give low viscosity liquids. Waxes are insoluble in water but soluble in organic, nonpolar solvents.SKU: n/a -
Chemicals
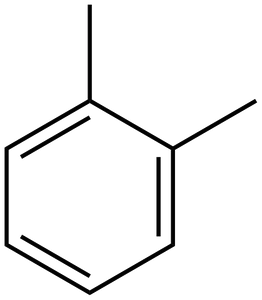
Xylene
Xylene is a colorless liquid that had a sweet odor.Xylene is flammable and practically insoluble. Xylene is primarily a synthetic chemical; however, it can occur naturally in petroleum, coal tar, and during forest fires. There are three forms of xylene: meta-xylene, ortho-xylene and para-xylene.Formula: C8H10SKU: n/a -
Chemicals
Yeast
Yeast are single-celled fungi. As fungi, they are related to the other fungi that people are more familiar with, including: edible mushrooms available at the supermarket, common baker’syeast used to leaven bread, molds that ripen blue cheese, and the molds that produce antibiotics for medical and veterinary use.
SKU: n/a -
Chemicals
Zinc Bromide
Zinc bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula ZnBr₂. It is a colourless salt that shares many properties with zinc chloride, namely a high solubility in water forming acidic solutions, and solubility in organic solvents. It is hygroscopic and forms a dihydrate ZnBr₂ · 2H₂O.Formula: ZnBr2SKU: n/a -
-
Chemicals
Zinc Chloride
Zinc chloride is the name of chemical compounds with the formula ZnCl₂ and its hydrates. Zinc chlorides, of which nine crystalline forms are known, are colorless or white, and are highly soluble in water. ZnCl₂ itself is hygroscopic and even deliquescent.Formula: ZnCl2SKU: n/a -
-
Chemicals
Zinc Hydroxide
Zinc hydroxide Zn(OH)₂ is an inorganic chemical compound. It also occurs naturally as 3 rare minerals: wülfingite, ashoverite and sweetite. Like the hydroxides of other metals, such as lead, aluminium, beryllium, tin and chromium, zinc hydroxide, is amphoteric.Formula: Zn(OH)2SKU: n/a